Using the collar option strategy means the investor keeps the cash credit, regardless of the price of the underlying stock when the options expire. Until the investor either exercises his put and sells the underlying stock, or is assigned an exercise notice on the written call and is obligated to sell his stock, all rights of stock ownership are retained. See both Protective Put and Covered Call strategies presented earlier in this section of the site. This example of a collar trade strategy assumes an accrued profit from the investor's underlying shares at the time the call and put positions are established, and that this unrealized profit is being protected on the downside by the long put.
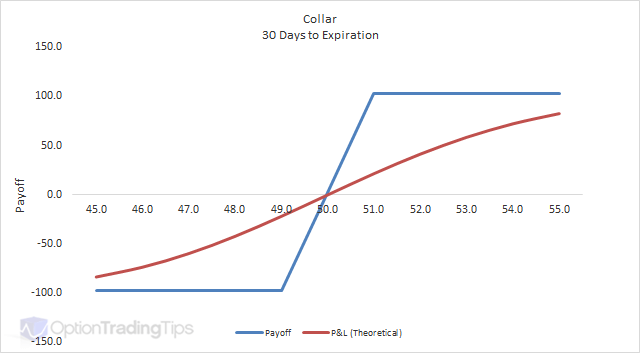
Therefore, discussion of maximum loss does not apply. Compare that to the net price received at expiration on the downside from exercising the put and selling the underlying shares, or the net sale price of the stock on the upside if assigned on the written call option. This example also assumes that when the combined position is established, both the written call and purchased put are out-of-the-money. If the underlying stock price is between the strike prices of the call and put when the options expire, both options will generally expire with no value.
In this case, the investor will lose the entire net premium paid when establishing the combination, or keep the entire net cash credit received when establishing the combination.
The Collar options Strategy Payoff Chart
Balance either result with the underlying stock profits accrued when the spread was established. An investor will employ the collar option strategy after accruing unrealized profits from the underlying shares, and wants to protect these gains with the purchase of a protective put. In this case, consideration of BEP does not apply. The effect of an increase or decrease in the volatility of the underlying stock may be noticed in the time value portion of the options' premiums.
The effect of time decay on the collar option strategy varies with the underlying stock's price level in relation to the strike prices of the long and short options. If the stock price is midway between the strike prices, the effect can be minimal. If the stock price is closer to the lower strike price of the long put, losses generally increase at a faster rate as time passes. Alternatively, if the underlying stock price is closer to the higher strike price of the written call, profits generally increase at a faster rate as time passes.
The combination may be closed out as a unit just as it was established as a unit. To do this, the investor enters a combination order to buy a call with the same contract and sell a put with the same contract terms, paying a net debit or receiving a net cash credit as determined by current option prices in the marketplace. If the underlying stock price is between the put and call strike prices when the options expire, the options will generally expire with no value.
- macro trading and investment strategies macroeconomic arbitrage in global markets.
- Collar Options Strategy ( Best Guide Collar Option Strategy Examples).
- como crear una cuenta demo en forex;
- forex us brokers.
The investor will retain ownership of the underlying shares and can either sell them or hedge them again with new option contracts. If the stock price is below the put's strike price as the options expire, the put will be in-the-money and have value. The investor can elect to either sell the put before the close of the market on the option's last trading day and receive cash, or exercise the put and sell the underlying shares at the put's strike price.
Alternatively, if the stock price is above the call's strike price as the options expire, the short call will be in-the-money and the investor can expect assignment to sell the underlying shares at the strike price. Or, if retaining ownership of the shares is now desired, the investor can close out the short call position by purchasing a call with the same contract terms before the close of trading. Learn more about the options market in Firstrade's guide to options strategies.
- Collar Definition.
- forex warning.
- Mutual Funds and Mutual Fund Investing - Fidelity Investments.
- Collar (Protective Collar).
Open your account today. All Rights Reserved. Visit us online at www. Powered by.
Definition of 'Collar Options'
Suggest a new Definition Proposed definitions will be considered for inclusion in the Economictimes. Circuit Breakers Definition: Circuit breakers are pre-defined values in percentage terms, which trigger an automatic check when there is a runaway move in any security or index on either direction. The values are calculated from the previous closing level of the security or the index. Usually, circuit breakers are employed for both stocks and indices. Many steps can possibly be taken after the breach of the circuit breakers. Some of the popular ones are: 1.
Halting of trade in a security or index for a certain period 2. Halting of trade in a security or index for the entire trading day. In case of the first option, trading in the security is halted for a few minutes to few hours to allow trading activity to cool down among the market participants.
This time period also allows market participants to absorb any sudden news development in a particular security or a set of securities and, thereafter, take a rational and measured approach towards the security during the rest of the trading session. If the volatility or big moves are still not controlled when trading resumes after a temporary halt, then the second option is invoked and trading is halted for the entire day. The percentage levels at which these circuit breakers are invoked are revised regularly, depending on the levels of the security or the index over a period.
Collar (finance)
For example, a stock may have a circuit breaker at 20 per cent for certain period and, subsequently, it can be revised downward to 10 per cent as the stock exchange may deem fit. Drawback: 1. The first downside of circuit breakers is that they prevent true price discovery in a stock both on its way up or down, at least for the limited time period they are imposed. Secondly, they allow early investors usually well-informed institutions or algo traders to gain advantage and make a move before circuit breakers are eventually invoked, thereby restricting the moves of other investors, who make a move a little later in the day usually retail investors.
Description: Circuit breakers are in place for various stocks on the Indian bourses. The usual values of these are 2 per cent, 5 per cent, 10 per cent or 20 per cent. Stocks that are traded in the derivatives segment do not have any circuit breakers. On the Indian stock exchanges, an index-based market-wide circuit breaker system applies at three stages of the index movement on either side, viz.
These circuit breakers, when triggered, bring about a coordinated trading halt in all equity and equity derivative markets nationwide. Market-wide circuit breakers are triggered by movement of either the BSE Sensex or the Nifty50, whichever hits the trigger first. After index-based market-wide circuit filter is breached, the market re-opens with a pre-open call auction session. The extent of the duration of the market halt and pre-open session is as given below Contra Fund Definition: A contra fund is defined by its against-the-wind kind of investing style.
The manager of a contra fund bets against the prevailing market trends by buying assets that are either under-performing or depressed at that point in time. This is done with the belief that the herd mentality followed by investors on the Street will lead to mispricing of assets, which will pick up steam in the long run, creating opportunities for investors to generate superlative returns.
Description: A contra fund is distinguished from other funds by its style of investing. A contra fund takes a contrarian view of an asset, when it either witnesses exuberant demand from investors or is shunned by them at a particular point in time due to short-term triggers. The underlying assumption is that the asset will stabilise and come to its real value in the long term once the short-term concerns plaguing it either become irrelevant or are mitigated.
The idea is to buy assets at a cost lower than its fundamental value in the long term. Investors must take note of the fact that contra funds may not perform in the short term because of the kind of assets they invest in. The contra fund may pick up stocks that are out of favour or invest in sectors that are witnessing a slump. A fund that seeks to capitalise on a commodities slump by picking up stocks in companies belonging to the sector can be called a contra fund.
Definition: The Collar Options strategy involves holding of shares of an underlying security while simultaneously buying protective Puts and writing Call options for the same underlying. The addition of a Protective Put safeguards the investor from large losses due to unexpected exponential fall in the price of the underlying.
Free calls on Social Media
In a Covered Call strategy, the quantum of risk embedded in the trade is limited but large. An option trader can hedge the risk of loss by buying a Put option. For this reason, Option Collars are also called Hedge Wrappers. In this strategy, the quantum of both risk and reward is limited. The outlook of the Collar Options trader for an underlying security is neutral.
The Collar Strategy Explained | Online Option Trading Guide
Description: In a Call option trade, the two counterparties involved are a Call Option writer and a Call Option buyer. The two parties have counter-views on the direction of the security price. The Call Option buyer believes the price of the underlying security is going to rise while the Call Option writer feels the price of the underlying security is going to fall.
An option writer is bound to sell the underlying at the same strike price in which the option buyer exercises his right. The option buyer will exercise his right only if it has an intrinsic value.